Vitamin B5: Comprehensive Nutrient Guide on Pantothenic Acid
Discover everything you need to know about Vitamin B5 in this comprehensive nutrient guide.

Vitamin B5, also known as pantothenic acid, is an essential nutrient that plays a pivotal role in human health. This water-soluble vitamin is crucial for synthesizing coenzyme-A (CoA), which is involved in various metabolic pathways. This nutrient guide delves into the intricacies of Vitamin B5, its benefits, sources, deficiency symptoms, and more.
The Role of Vitamin B5 in the Body
Vitamin B5 is indispensable for the proper functioning of the human body. It is involved in the production of blood cells, and it aids in converting the food we eat into energy. It also plays a significant role in synthesizing fats, steroids, and several other vital substances.
Moreover, Vitamin B5 is essential for the production of cholesterol and certain hormones in the adrenal glands. It is also involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and the metabolism of drugs and toxins -- it is clear that Vitamin B5 is integral to our overall health and wellbeing.
Metabolism and Energy Production
Vitamin B5 is a key player in the metabolism of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. It forms a part of the coenzyme-A (CoA), which is involved in several metabolic pathways that generate energy from food. This is why adequate intake of Vitamin B5 is crucial for maintaining energy levels and overall metabolic health.
Furthermore, Vitamin B5 is involved in synthesizing fatty acids, which are essential for producing energy in the body. It also aids in the production of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body, further contributing to energy production and endurance.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Vitamin B5 offers a plethora of health benefits. From skin health to mental well-being, this vitamin involves numerous physiological processes contributing to our overall health.
Research suggests that Vitamin B5 can help reduce the signs of skin aging, improve wound healing, and even reduce acne. It is also believed to improve heart health, boost immunity, and enhance mental performance. Let's delve deeper into these benefits.
Skin Health
Vitamin B5 is often found in skincare products due to its moisturizing, soothing, and healing properties. It helps to keep the skin soft, smooth, and healthy. Moreover, it has anti-inflammatory effects, which can help soothe irritated skin.
Research has also shown that Vitamin B5 can help improve the skin's barrier function, which helps to keep harmful substances out and moisture in. This can help to prevent skin conditions such as eczema and dermatitis.
Heart Health
Vitamin B5 plays a crucial role in the production of coenzyme A, which is involved in the synthesis of cholesterol. This implies that Vitamin B5 may help regulate cholesterol levels in the body, promoting heart health.
Moreover, some studies suggest that Vitamin B5 can help reduce the risk of heart disease by lowering bad cholesterol levels and increasing good cholesterol levels. However, more research is needed in this area to confirm these findings.
Sources of Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
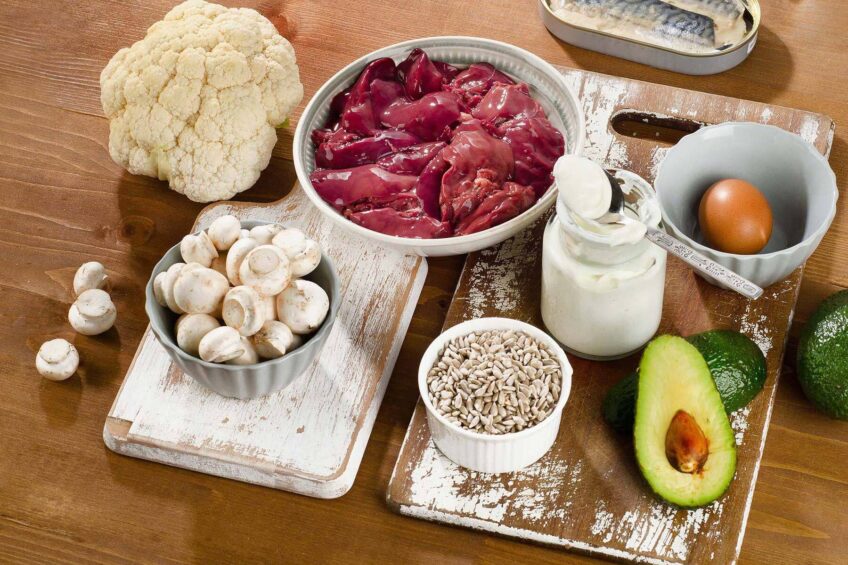
Vitamin B5 is widely distributed in both animal and plant foods. Some of the richest sources of this vitamin include meat, eggs, legumes, whole grains, and vegetables.
It's important to note that cooking can reduce the Vitamin B5 content in foods. Hence, to maximize your intake of this vitamin, it's best to consume foods in their raw form or cook them using methods that minimize nutrient loss.
Animal Sources
Animal foods are excellent sources of Vitamin B5. This includes poultry, beef, seafood, caviar, and eggs. Organ meats such as liver and kidney are particularly rich in this vitamin.
Dairy products like milk, cheese, and yogurt contain significant amounts of Vitamin B5. However, the vitamin content can vary depending on the type of dairy product and how it's processed.
Plant Sources
Many plant foods also provide Vitamin B5. This includes whole grains, legumes, avocados, and potatoes. Vegetables like broccoli and kale are also good sources of this vitamin. Sunflower seeds, shiitake mushrooms, and grape leaves are good sources but require more daily servings.
Nuts and seeds are another excellent source of Vitamin B5. They provide this essential vitamin and offer a host of other nutrients, making them a great addition to a healthy diet.
Managing Pantothenic Acid Intake
- Recommended Intake: Aim for 10 mg per day for optimal health benefits. The easiest way to meet this is with two heaping teaspoons of unfortified nutritional yeast.
- Food vs. Supplements: While food sources are superior, supplements like pantothenic acid, mineral salts labeled as pantothenate, and pantethine are effective for most people.
- Acne: High doses of pantothenic acid and topical applications (1000-10,000 mg applied 4-6 times daily) can treat acne.
- Cholesterol: Pantethine effectively lowers cholesterol levels at 600-1200 mg daily.
Vitamin B5 Deficiency
While Vitamin B5 deficiency is rare due to its widespread availability in foods, it can occur in certain situations. Symptoms of deficiency can include fatigue, depression, irritability, nausea, and muscle cramps.
Severe deficiency can lead to a condition known as pantothenic acid deficiency syndrome, which is characterized by insomnia, stomach problems, and numbness in the hands and feet. However, this condition is extremely rare and is usually seen only in severe malnutrition.
More severe deficiency causes poor mood, childish behavior, numbness or tingling in the hands and feet, insomnia, elevated heart rate in response to minor exertion, abdominal cramps, gas, nausea, and vomiting.
Risk Factors for Deficiency
Although Vitamin B5 deficiency is rare, certain factors can increase the risk. This includes a diet low in fresh fruits and vegetables, excessive consumption of processed foods, and certain medical conditions that affect nutrient absorption.
People with alcohol dependence are also at a higher risk of Vitamin B5 deficiency, as alcohol can interfere with the absorption and metabolism of this vitamin. Therefore, it's critical for these individuals to ensure adequate intake of Vitamin B5.
Conclusion
Vitamin B5, or pantothenic acid, is a vital nutrient with a broad spectrum of roles, from supporting energy production to maintaining mental and physical health.
A diet rich in nutritional yeast, organ meats, and other B5-rich foods, along with appropriate supplementation, can ensure adequate pantothenic acid intake.
Understanding and managing pantothenic acid intake is key to preventing deficiency-related conditions and optimizing health benefits. As with any supplementation, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended for personalized advice.