Vitamin C: Comprehensive Nutrient Guide on Ascorbic Acid
Discover the benefits of Vitamin C in this comprehensive nutrient guide. Learn about its sources, recommended intake, and potential side effects.
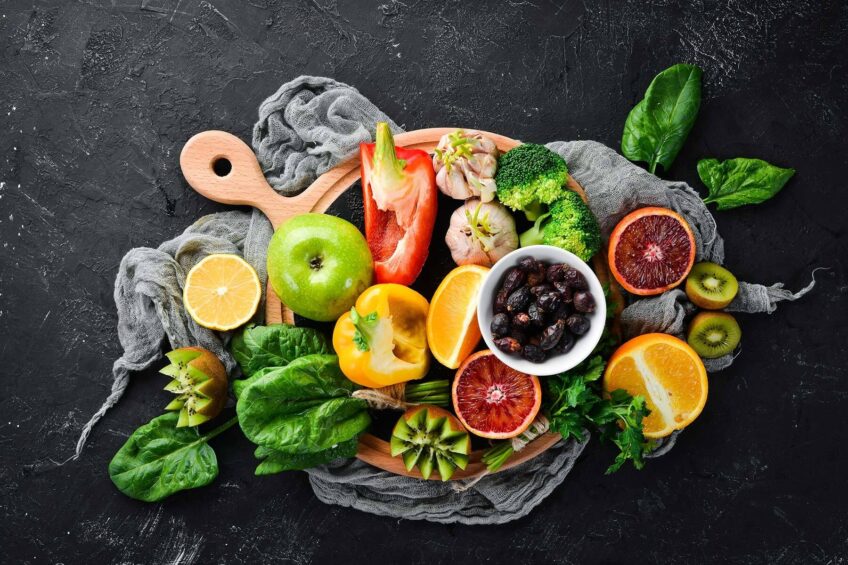

Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in numerous bodily functions, far beyond the well-documented prevention of scurvy. This nutrient guide aims to provide an in-depth understanding of Vitamin C, its benefits, sources, and importance to human health.
The Importance of Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient that the body cannot produce on its own. It plays a crucial role in the body's immune function, aiding in the production of white blood cells, which help fight off infections. Furthermore, it is a potent antioxidant, protecting cells from harmful free radicals.
Additionally, Vitamin C is necessary for the production of collagen, a protein that helps wounds heal and maintains the health of skin, teeth, bones, and blood vessels. It also enhances the body's ability to absorb iron, a mineral essential for red blood cell production and oxygen transportation.
Sources of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
While the body cannot produce Vitamin C, it can be obtained through diet and supplements. Fruits and vegetables are the best sources of this nutrient, with citrus fruits, strawberries, bell peppers, and broccoli particularly rich in Vitamin C.
Supplements can also provide Vitamin C, especially for those who struggle to consume enough through their diet. However, it's important to note that supplements should not replace a balanced diet, and it's always best to get nutrients from food sources when possible.
Dietary Sources
Citrus fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are well-known sources of Vitamin C. Other fruits like strawberries, kiwis, and pineapples also contain significant amounts. Regarding vegetables, bell peppers, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts are excellent sources.
It's important to note that cooking can reduce the Vitamin C content in food. Therefore, consuming these fruits and vegetables raw or lightly cooked can help maximize their Vitamin C content.
Supplemental Sources
Vitamin C supplements come in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and powders. These can benefit individuals with certain health conditions or dietary restrictions that make it difficult to get enough Vitamin C from food.
However, it's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement regimen, as excessive intake can lead to side effects like diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps.
Benefits of Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
Vitamin C offers numerous health benefits due to its role in various bodily functions. Its antioxidant properties help protect cells from damage, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
Its role in collagen production helps maintain skin health, potentially slowing the aging process and healing wounds. Furthermore, by enhancing iron absorption, Vitamin C can help prevent anemia, a condition characterized by a lack of healthy red blood cells.
Preventing Scurvy
Vitamin C is essential for avoiding the common symptoms of scurvy-like bleeding gums, bruise-like marks, and corkscrew hair patterns, as well as serious consequences like heart attacks and internal bleeding.
Immune Function
Vitamin C's role in immune function is perhaps its most well-known benefit. It aids in the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for fighting off infections. Additionally, as an antioxidant, it protects these cells from damage, enhancing their effectiveness.
Research has shown that Vitamin C can help reduce the duration and severity of common cold symptoms. While it may not prevent colds, regular intake can help ensure the immune system functions at its best.
Skin Health
As a key player in collagen production, Vitamin C is vital for skin health. Collagen is a protein that gives skin its elasticity and strength. As we age, collagen production decreases, leading to wrinkles and sagging skin.
Topical Vitamin C has been shown to stimulate collagen production, potentially slowing the aging process. Additionally, its antioxidant properties can help protect the skin from damage caused by environmental factors like sun exposure and pollution.
Cancer Prevention
Research in epidemiology indicates a correlation between increased consumption of fruits and vegetables and a reduced risk of various cancer types. This protective effect is partially attributed to their high Vitamin C content, which plays a multifaceted role in cancer prevention:
- Inhibition of Carcinogen Formation: It can limit the formation of carcinogens like nitrosamines, reducing cancer risk.
- Immune System Modulation: Vitamin C may influence the immune response, enhancing the body's ability to combat precancerous conditions.
- Antioxidant Function: As an antioxidant, Vitamin C potentially reduces oxidative damage, a known contributor to cancer development.
Inverse associations have been observed between dietary Vitamin C intake and cancers of the lung, breast, colon, rectum, stomach, oral cavity, larynx, pharynx, and esophagus. Additionally, lower plasma concentrations of Vitamin C are often found in individuals with cancer compared to healthy controls, further underscoring its potential role in cancer prevention.
Managing Vitamin C Intake
People with a history of kidney stones, hemochromatosis, or glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency should be careful with Vitamin C supplements.
- Daily Requirements: 10 mg/d is sufficient to prevent scurvy, while 100-140 mg/d is associated with the lowest risk of cancer and heart disease.
- Higher Intake for Specific Needs: 250 mg/d may be necessary for those under extreme stress or engaging in intense exercise, and 400 mg/d can provide the highest achievable blood levels.
- Supplementation: If dietary intake is insufficient, supplementing with 100-200 mg of Vitamin C once or twice daily is recommended.
Some may discover that buffered Vitamin C formulations are more agreeable to their gastrointestinal system or that liposomal Vitamin C demonstrates greater efficacy in cold prevention.
Potential Risks and Considerations
While Vitamin C is essential for health, it's important to be mindful of potential risks and considerations. Overconsumption can lead to side effects, and certain populations may need to be cautious with their intake.
Furthermore, while Vitamin C supplements can benefit some, they are unnecessary for everyone. It's always best to consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement regimen.
Overconsumption
While Vitamin C is water-soluble and excess amounts are excreted through urine, consuming too much can lead to gastrointestinal discomfort, including diarrhea, nausea, and stomach cramps. These side effects are more common with supplement use, as it's easier to consume large amounts in this form.
Long-term overconsumption can also lead to kidney stones in individuals with a history of this condition. Therefore, it's important to stick to the recommended daily intake unless advised otherwise by a healthcare professional.
Special Populations
Certain populations may need to be cautious with their Vitamin C intake. For instance, individuals with kidney disease may need to limit their intake, as high levels can lead to kidney stones. Additionally, people with a certain type of iron overload disease should avoid Vitamin C supplements, as they can increase iron absorption, worsening the condition.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women may need higher amounts of Vitamin C to support the growth and development of their babies. However, they should consult a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate amount.
Conclusion
Vitamin C is a vital nutrient that plays a significant role in numerous bodily functions, including immune function, collagen production, and iron absorption. While it can be obtained through diet and supplements, it's important to be mindful of potential risks and considerations, including overconsumption and special population needs.
As always, it's best to consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet or supplement regimen. With the right approach, Vitamin C can be a powerful tool in maintaining and enhancing health.