Omega-3: EPA, DHA, and ALA Fatty Acids Nutrient Guide
Discover everything you need to know about Omega-3 fatty acids in our comprehensive nutrient guide.

Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of fat that is crucial for human health. They are primarily found in fish, seafood, and some plant foods. Despite their importance, most people do not consume enough of these essential nutrients. This article will delve into the science behind Omega-3, its health benefits, sources, and recommended intake.
The Science Behind Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids are polyunsaturated fats, a type of fat your body can't make. The term "polyunsaturated" refers to their chemical structure, as "poly" means many, and "unsaturated" indicates that the fatty acids have several double bonds.
There are three types of Omega-3 fatty acids: eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). EPA and DHA are primarily found in fish, while ALA is mostly found in plant foods such as flaxseeds and walnuts.
Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA)
EPA is a 20-carbon fatty acid that plays a crucial role in the cardiovascular system. It helps reduce inflammation and prevent blood clots. EPA is primarily found in fatty fish and fish oil.
Studies have shown that EPA can help lower symptoms of depression and improve mood. It may also aid in weight management by reducing body fat.
Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA)
DHA is a 22-carbon fatty acid that is vital for brain health. It is a key component of the cell membranes in the brain and is necessary for proper brain development and function.
DHA has been linked to improved memory, learning, and behavior. It may also help prevent age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease.
Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA)
ALA is an 18-carbon fatty acid that can be converted into EPA and DHA in the body, although this process is not very efficient. ALA is mainly used by the body for energy.
ALA has been associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease. It may also have anti-inflammatory effects and help improve lung function.
Health Benefits of Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids have been studied extensively for their health benefits. They have been found to have a positive impact on various aspects of health, from heart and brain health to mental health and inflammation.
Here are some key health benefits of Omega-3:
- Heart Health: can reduce triglycerides, lower blood pressure, reduce blood clotting, decrease stroke and heart failure risk, and reduce irregular heartbeats.
- Brain Health: plays a crucial role in brain function and development. They can also boost brain health during aging and help prevent mental decline.
- Mental Health: can help reduce symptoms of schizophrenia, depression, bipolar disorder, and ADHD.
- Inflammation: can reduce the production of molecules and substances linked to inflammation.
- Autoimmune Diseases: can help fight several autoimmune diseases, including type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and psoriasis.
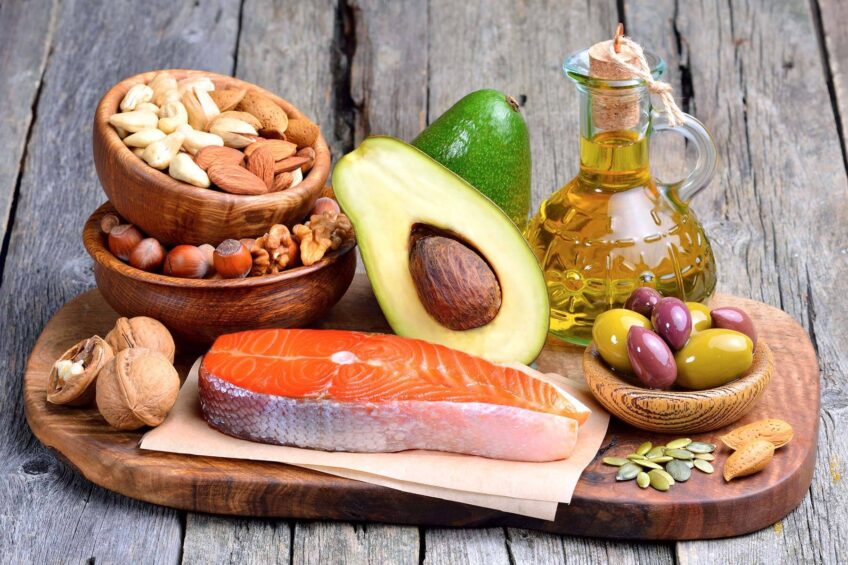
Sources of Omega-3
Omega-3 fatty acids are found in a variety of foods. However, it's important to note that not all Omega-3 fatty acids are created equal. While ALA is found in many plant foods, EPA and DHA are primarily found in certain types of fish.
Here are some of the best sources of Omega-3:
- Fish and Other Seafood: Salmon, mackerel, tuna, herring, and sardines are the most potent sources of Omega-3.
- Nuts and Seeds: Flaxseeds, chia seeds, walnuts, and hemp seeds are rich in ALA.
- Fortified Foods: Some foods are fortified with Omega-3, including certain brands of eggs, yogurt, juices, milk, and soy beverages.
While plant oils, such as flaxseed oil, soybean oil, and canola oil, are among the best plant sources of Omega-3, these sources should be highly limited or avoided altogether.
Fish oil or cod liver oil can be used. Cod liver oil has the benefit of extra Vitamin A and Vitamin D.
Recommended Intake of Omega-3
The recommended intake of Omega-3 varies depending on age, sex, and life stage. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a daily intake of 0.2-0.5 grams of EPA and DHA for adults, while the American Heart Association recommends eating at least two servings of fish per week.
For ALA, the adequate intake is 1.6 grams per day for men and 1.1 grams per day for women. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should aim for 1.4 grams and 1.3 grams per day, respectively.
The intake recommendations vary:
- General: Most adults should consume 150 mg/d DHA per week from pasture-raised egg yolks or fatty fish.
- Children: Breastfeeding is recommended, followed by a DHA-rich diet up to age 4.
- Specific Health Conditions: Higher doses may be beneficial for conditions like ADHD, depression, and high triglycerides.
Special Considerations
- Conversion Efficiency: Factors such as genetics, health conditions, and diet can affect the conversion of ALA to DHA and EPA.
- Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio: Balancing this ratio is crucial, especially for those relying on plant oils.
- Supplementation: For those not consuming fish, liver, or egg yolks, supplements like fish oil, cod liver oil, or vegan options should be considered.
- High Triglycerides: up to 5 grams of EPA daily may be helpful.
- Vegans: Consider supplements from the fungus Mortierella alpina, as mentioned in our Omega-6 guide, or DHA supplements from algal oil.
It's important to note that these are general recommendations, and individual needs may vary. Always consult with a healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
Conclusion
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in human health. They offer numerous health benefits, including improved heart and brain health, reduced inflammation, and potential protection against autoimmune diseases.
Incorporating foods rich in EPA, DHA, and ALA into your diet is crucial for ensuring adequate intake of these vital nutrients.
Despite their importance, most people do not consume enough Omega-3 in their diet. By incorporating foods rich in EPA, DHA, and ALA into your diet, you can ensure you are getting enough of these essential nutrients.