Omega-6: Comprehensive Fatty Acid Nutrient Guide
Unlock the secrets of omega-6 fatty acids with our comprehensive nutrient guide. Learn about its role in the body, sources, benefits, and potential risks.

Omega-6 fatty acids are a group of polyunsaturated fats (PUFAs) that are essential for human health. They play a crucial role in brain function and normal growth and development. As the body cannot produce them, they must be obtained from dietary sources.
This nutrient guide delves into the science behind Omega-6 fatty acids, their benefits, sources, and the balance between Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids. It also explores the potential implications of excessive Omega-6 consumption.
The Science Behind Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that is present in many types of food. They are called "essential" fatty acids because our bodies cannot make them, so we need to get them from our diet.
There are several types of Omega-6 fatty acids, and they all have different roles within the body. Linoleic acid (LA) is the most common type, and it can be converted into other Omega-6 fats, such as arachidonic acid (AA).
Biological Role of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids are involved in many bodily functions, including cell growth, brain development, and inflammation. They are also part of the cell membrane and play a role in the functioning of the cell receptors.
Arachidonic acid, a derivative of linoleic acid, is used by the body to produce eicosanoids, which are signaling molecules that have diverse functions in the body's cardiovascular, pulmonary, immune, and endocrine systems.
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential for various physiological processes:
- Essential Fatty Acid Deficiency: A deficiency in Omega-6 can lead to issues like dandruff, inflamed skin, hair loss, low libido, infertility, and hormonal imbalances.
- Importance of Arachidonic Acid: This Omega-6 fatty acid is vital for stomach health, preventing food intolerances, infection defense, resolving chronic inflammation, and maintaining mental well-being.
Metabolism of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids are metabolized in the body through a series of enzymatic reactions. The first step is the conversion of linoleic acid into gamma-linolenic acid (GLA) by the enzyme delta-6-desaturase (D6D).
GLA is then further metabolized into dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA), which can be converted into arachidonic acid (AA). These conversions are facilitated by the enzymes elongase and delta-5-desaturase (D5D).
Benefits of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential for good health. They provide numerous benefits, including promoting brain health, stimulating skin and hair growth, maintaining bone health, regulating metabolism, and maintaining the reproductive system.
Research has also suggested that Omega-6 fatty acids may have protective effects against certain diseases, including heart disease, arthritis, and cancer. However, more research is needed to understand these potential benefits fully.
Omega-6 and Heart Health
Some studies suggest that Omega-6 fatty acids may help reduce the risk of heart disease. They can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increase HDL (good) cholesterol levels. They may also help reduce inflammation, which is a risk factor for heart disease.
However, the relationship between Omega-6 fatty acids and heart health is complex and not fully understood. Some research suggests that a high intake of Omega-6 fatty acids, particularly arachidonic acid, may increase inflammation and the risk of heart disease. Therefore, it's important to maintain a balance between Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids in the diet.
Omega-6 and Inflammation
Omega-6 fatty acids are known to play a role in the body's inflammatory response. Some types of Omega-6 fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid, can be converted into pro-inflammatory eicosanoids. However, other types of Omega-6 fatty acids, such as DGLA, can be converted into anti-inflammatory compounds.
This dual role of Omega-6 fatty acids in inflammation highlights the importance of maintaining a balance between different types of Omega-6 fatty acids, as well as a balance between Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids.
Sources of Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-6 fatty acids are found in a variety of foods. The richest sources are seed oils, such as sunflower, corn, soybean, and cottonseed oil. It's important to note that while these foods are good sources of Omega-6 fatty acids, they should be strictly avoided.
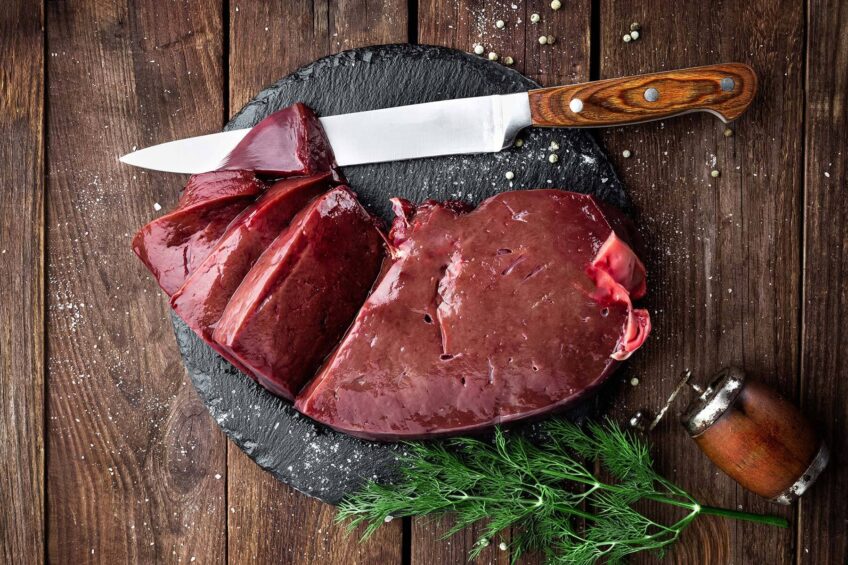
Preferred food sources include nuts, seeds, and meat. Beef liver is especially high in arachidonic acid and helps with EFA deficiency.
Overconsumption of Omega-6 fatty acids, particularly in the form of processed foods and fried foods, can lead to an imbalance in the Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio and potentially contribute to inflammation and other health problems.
A balanced intake of Omega-6 can be achieved through various dietary sources:
- Linoleic Acid and Arachidonic Acid: Linoleic acid, found in many natural foods, is a precursor to arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is found in egg yolks and liver.
- Supplementation: Arachidonic acid supplements, often derived from the mushroom Mortierella alpina, are available for those who need them, such as Vegans.
Managing Omega-6 Intake
- Recommended Intake: For most individuals, 1 gram of linoleic acid or 130 mg of arachidonic acid per 2000 Calories is sufficient.
- Vulnerable Groups: Growing children, pregnant or nursing mothers, those who train regularly with weights, and individuals recovering from illness or injury should pay particular attention to Omega-6 intake.
- Conversion Factors: Genetic factors, health conditions like diabetes, and dietary choices can affect the conversion of linoleic acid to arachidonic acid.
Omega-6 and Omega-3 Balance
The balance between Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids in the diet is important for maintaining good health. Both types of fatty acids are essential, but they have different roles in the body and need to be balanced to function optimally.
Historically, the human diet had a ratio of Omega-6 to Omega-3 fatty acids of approximately 1:1. However, in Western diets today, this ratio is often significantly higher, with some estimates suggesting a ratio of 16:1. This imbalance may contribute to the development of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Important considerations with balancing Omega fatty acids:
- Activation of Arachidonic Acid: Impaired by NSAIDs, acetaminophen, and natural anti-inflammatories. EPA from fish oil can also affect activation.
- Balancing with Omega-3: High intake of total PUFAs, including Omega-3, can reduce the conversion of Omega-6 fatty acids.
- Vitamin E Requirement: All PUFAs, including Omega-6, increase the need for Vitamin E. It's important not to exceed the necessary intake of EFAs to avoid excessive Vitamin E requirements.
How to Achieve a Balanced Omega-6 to Omega-3 Ratio
Achieving a balanced Omega-6 to Omega-3 ratio is not just about reducing Omega-6 intake but also about increasing Omega-3 intake. This can be done by eating more Omega-3-rich foods, such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, and by reducing the intake of Omega-6-rich foods, mainly processed and fried foods.
Supplements can also be used to increase Omega-3 intake, but they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional. It's also important to remember that balance is key, and both Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for good health.
Conclusion
Omega-6 fatty acids are essential nutrients that play a crucial role in brain function and cell growth. They are also involved in the body's inflammatory response and may have protective effects against certain diseases. However, it's important to maintain a balance between Omega-6 and Omega-3 fatty acids to ensure optimal health.
Understanding the science behind Omega-6 fatty acids, their benefits, and their sources can help individuals make informed dietary choices. With the right balance, Omega-6 fatty acids can contribute to a healthy and balanced diet.