Vitamin B7: Comprehensive Nutrient Guide to Biotin
Discover everything you need to know about Vitamin B7, the beauty vitamin known as biotin, in this comprehensive nutrient guide.

Vitamin B7, known as biotin, is a crucial nutrient in maintaining optimal health. This water-soluble vitamin is part of the B-vitamin complex, which aids in converting food into energy. This article delves into the intricacies of Vitamin B7, its benefits, sources, and potential side effects.
The Importance of Vitamin B7
Vitamin B7 is integral to several physiological functions. It is essential for metabolizing carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, thereby contributing to energy production. It also plays a significant role in maintaining the health of the skin, hair, and nails.
Moreover, Vitamin B7 is involved in gene regulation and cell signaling, and it aids in the development and functioning of several bodily systems, including the nervous system. It is also crucial for pregnant women, as it supports embryonic growth and prevents congenital disabilities.
Role in Metabolism
Vitamin B7 acts as a coenzyme in the body, assisting in the metabolism of macronutrients. It helps break down complex substances like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into simpler forms that the body can utilize for energy. Without adequate Vitamin B7, these metabolic processes can be hindered, leading to various health issues.
Furthermore, Vitamin B7 aids in the synthesis of glucose, which is a primary source of energy for the body. It also supports the production of fatty acids essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system.
Role in Skin, Hair, and Nail Health
Vitamin B7 is often referred to as the beauty vitamin due to its significant impact on skin, hair, and nail health. It aids in the production of keratin, a protein that forms the structural component of hair, skin, and nails.
Deficiency in Vitamin B7 can lead to symptoms like hair loss, brittle nails, and skin rashes. Therefore, adequate intake of this vitamin is crucial for maintaining healthy skin, hair, and nails.
Sources of Vitamin B7
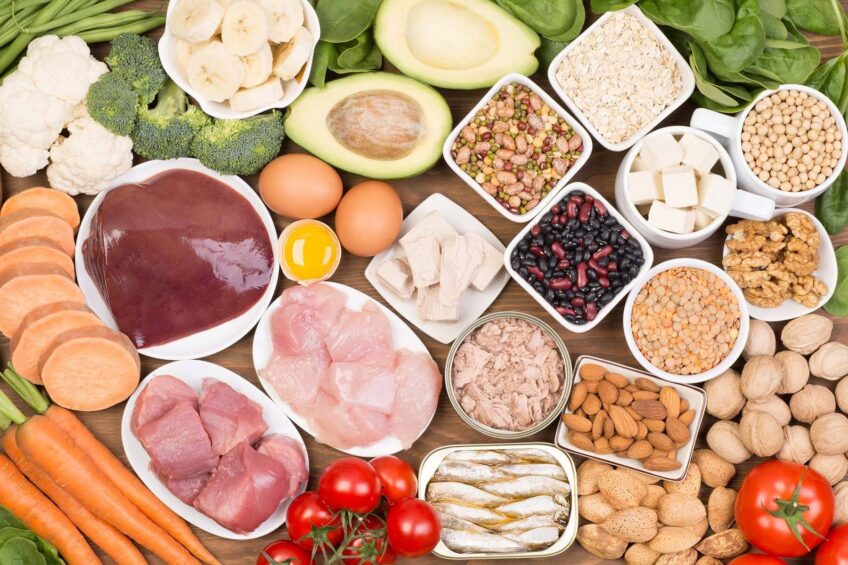
Vitamin B7 is widely available in a variety of foods. The best sources include organ meats, egg yolks, fish, meat, seeds, nuts, and certain vegetables. The body also produces some amount of Vitamin B7 in the gut.
However, the bioavailability of Vitamin B7 can vary depending on the source. It is more readily absorbed from animal-based sources than plant-based ones. Moreover, specific food processing methods can reduce the Vitamin B7 content in foods such as egg whites, which should be boiled for 4-8 minutes to deactivate avidin, a protein that binds to biotin.
Animal-Based Sources
Organ meats like liver and kidney are among the richest sources of Vitamin B7. Other animal-based sources include egg yolks, fish, and meat. Dairy products like milk and cheese also contain some amount of this vitamin.
It's important to note that the yolk contains most of the Vitamin B7 in eggs. The protein in egg whites can bind to Vitamin B7 and prevent its absorption. Therefore, consuming whole eggs is recommended to obtain the maximum benefits.
Plant-Based Sources
Nuts and seeds, particularly almonds, peanuts, and sunflower seeds, are good plant-based sources of Vitamin B7. Certain vegetables like sweet potatoes, spinach, and broccoli also contain this vitamin.
However, the bioavailability of Vitamin B7 from plant-based sources is lower than that from animal-based sources. Therefore, vegetarians and vegans may need to consume larger quantities of these foods to meet their Vitamin B7 requirements.
Managing Biotin Intake
High doses of biotin in the range ofthousands of micrograms per day have no toxicity. However, they can interfere with vitamin B5 and lipoic acid absorption. It is best to take such high doses of biotin only if needed to resolve deficiency symptoms.
- Recommended Intake: 150 micrograms per day for diets with up to 100 grams of non-collagen protein, increasing by 35 micrograms for every additional 50 grams of protein intake.
- Pregnant and Lactating Women: Should increase their intake by 1.7 times the calculated value to prevent deficiency and reduce the risk of birth defects.
Vitamin B7 (Biotin) Deficiency
Kidney disorders that require dialysis, along with digestive disorders and alcoholism, are clear indications of biotin deficiency.
- Symptoms: Include skin issues, hair loss, depression, tingling sensations, and in severe cases, loss of motor control and seizures.
- Increased Risk Factors: Pregnancy, dialysis, digestive disorders, alcoholism, and certain genetic conditions.
- Dietary Considerations: Focus on biotin-rich foods, especially those with biotin not bound to protein, like egg yolks and natto.
Potential Side Effects of Vitamin B7
While Vitamin B7 is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, excessive intake can lead to potential side effects. These may include skin rashes, digestive upset, insulin release, and kidney problems. It's important to note that these side effects are rare and typically occur only with high doses.
Moreover, Vitamin B7 can interfere with specific lab tests and lead to falsely elevated or decreased results. Therefore, informing healthcare providers about any Vitamin B7 supplements being taken is advisable.
In conclusion, Vitamin B7 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions. It's vital to ensure adequate intake of this vitamin through a balanced diet or supplements if necessary. As with any nutrient, it's advisable to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplementation regimen.